Product Description
Technical parameter for SD7 slewing drive, worm drive
1. Introduction of CHINAMFG slewing drive
Slewing Drive is also called slewing gear, worm gear, worm drive, rotary drive, slew drive, worm gear reducer and rotary drive unit. At present the majority of such devices are caller Slewing Drive.
CHINAMFG Slewing Drive movement can reduce power consumption, since the security role. In addition to the field of use in the daily solar power systems are usually used for Special vehicle, heavy-duty flat-panel truck, container cranes, truck mounted crane, automobile crane and aerial vehicles, cranes, gantry cranes, small wind power stations, space communications, satellite receiver, etc…The Slewing Drive in the solar photovoltaic industry, the general configuration DC planetary reduction motor or AC geared motors; Main configuration of the hydraulic motor as a power-driven construction machinery
CHINAMFG Slewing Drive principle of the large transmission ratio of the deceleration device to transmit motion and power between the 2 axes staggered in space. The Slewing Drive transmission is usually the case of the main components of the worm and wheel bearings, shell, and the power source
As the core component of turntable bearings, can withstand the axial load, radial load and overturning moment.
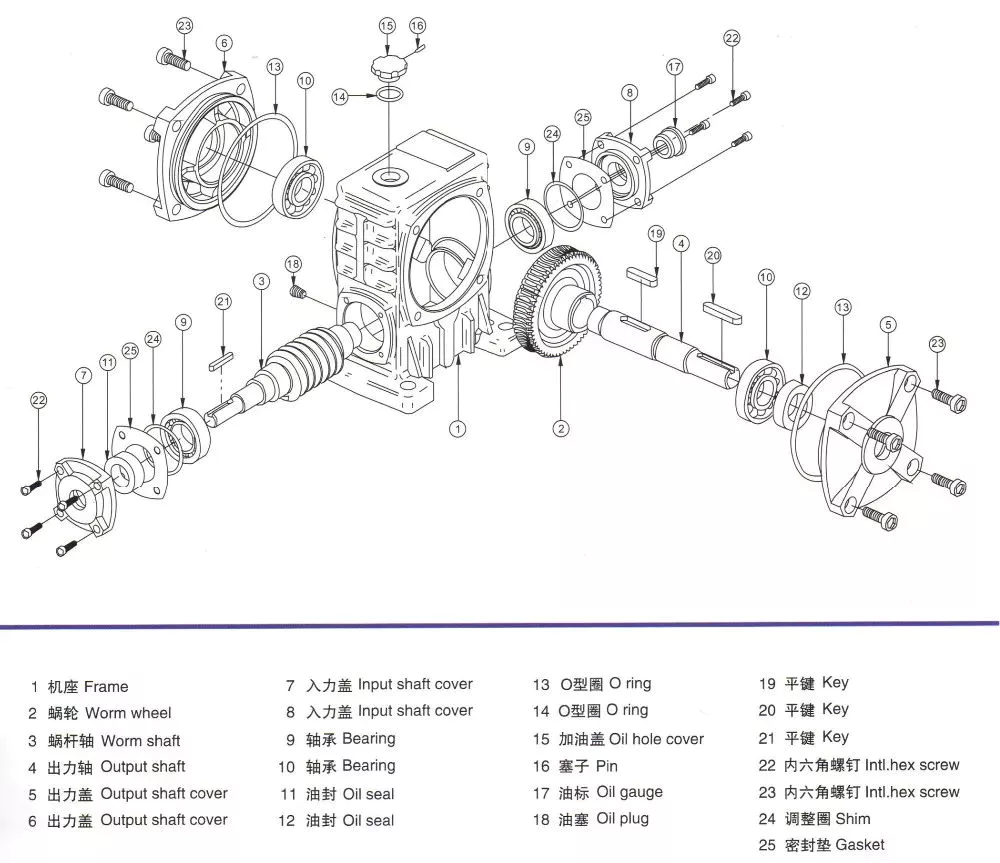
2. Structure
Slewing drive can be divided into 2 different structures as per different applications.
Light load slewing drive
Heavy load slewing drive
The dimensions of slewing drives include 3 inch, 5 inch, 7 inch, 9 inch, 12 inch, 14 inch, 17 inch, 21 inch and 25 inch.
3. Features:
Slewing drive is a special bearing. And a slewing drive usually consist of slewing bearing, worm shaft, housing, bearing, motor and so on. Motor drive the worm shaft, the outer ring of slewing bearing will rotate, the outer ring output the torque through flange while the inner ring of slewing bearing is fixed in housing.
CHINAMFG Slewing Drive and rotary products, compared with the ease of installation, ease of maintenance, Installation space savings advantages to a greater extent.
4. Application:
Slewing drives are widely used in aerospace area, solar power systems, wind turbines, satellite broadcasting system, and engineering machinery like truck cranes, and man lifts, etc. Recently years, it has been prosperously used in photovoltaic power generation systems, special vehicle, heavy-duty flat-panel truck, container cranes, truck mounted crane, automobile crane and aerial vehicles, cranes, gantry cranes, small wind power stations, space communications, satellite receiver, etc.
| Model | Rated output torque /KN-m | Tilting Moment torque /KN-m | Load /KN | Gear ratio | Self-locking gears | Boundary dimensions (mm) | Weight (KG) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Static load rating, axial | Static load rating,radial | Dynamic load rating, axial | Dynamic load rating,radial | L | L1 | L2 | L3 | H2 | H3 | H4 | ΦD | ΦD1 | ΦD2 | ΦD3 | ΦD4 | ΦD5 | n1-Y | n1-X | H | H1 | ||||||
| 3″ | 0.2 | 0.5 | 30 | 16.6 | 9.6 | 8.4 | 62:1 | yes | 346 | 153 | 114 | 80 | 14.5 | 60.5 | 125 | 100 | 100 | 126 | 6-M10 | 6-M10 | 190 | 109 | 12 | |||
| 5″ | 0.3 | 0.8 | 76 | 22.6 | 13.8 | 11.8 | 62:1 | yes | 361 | 168 | 128 | 93.7 | 24.6 | 7 | 38 | 161 | 135 | 103.5 | 70 | 50 | 120 | 6-M10 | 7-M10 | 219 | 79 | 18 |
| 7″ | 1 | 13.5 | 133 | 53 | 32 | 28 | 73:1 | yes | 398 | 182 | 166 | 132.7 | 23.4 | 4.3 | 42.5 | 237.5 | 203.2 | 163 | 120.6 | 98 | 145 | 8-M12 | 10-M12 | 295 | 81 | 23 |
| 9″ | 7.3 | 33.9 | 338 | 135 | 81 | 71 | 61:1 | yes | 546 | 314 | 239 | 174.1 | 29 | 4.4 | 54.5 | 316 | 270 | 222.5 | 175 | 145 | 204 | 16-M16 | 15-M16 | 411 | 108 | 50 |
| 12″ | 9.2 | 54.3 | 475 | 190 | 114 | 100 | 78:1 | yes | 556 | 324 | 285 | 220 | 27 | 4.4 | 58.5 | 401.5 | 358 | 308.5 | 259 | 229 | 289 | 18-M16 | 19-M16 | 500 | 110.5 | 60 |
| 14″ | 10.5 | 67.8 | 555 | 222 | 133 | 117 | 85:1 | yes | 547 | 330 | 303 | 238 | 28 | 3.5 | 59 | 435.5 | 390 | 342.5 | 295 | 265 | 325 | 18-M16 | 23-M16 | 530 | 110 | 73 |
| 17″ | 14.5 | 135.6 | 975 | 390 | 235 | 205 | 102:1 | yes | 555 | 338 | 340 | 275.3 | 26 | 4.6 | 66 | 522 | 479.4 | 425.5 | 365.1 | 324 | 406 | 20-M16 | 20-M16 | 615 | 126 | 110 |
| 21″ | 20.2 | 203 | 1598 | 640 | 385 | 335 | 125:1 | yes | 678 | 461 | 398 | 333 | 3.3 | 4.5 | 76 | 616 | 584.2 | 525.5 | 466.7 | 431.8 | 532 | 36-M20 | 35-M20 | 732 | 136.5 | 158 |
| 25″ | 22.5 | 271 | 2360 | 945 | 590 | 470 | 150:1 | Yes | 678 | 461 | 467 | 401.8 | 6.2 | 4.5 | 78.2 | 744 | 675 | 620 | 585 | 512 | 628.5 | 36-M20 | 35-M20 | 863 | 133.2 | 230 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Feature: | Longlife |
|---|---|
| Step: | Single-Step |
| Layout: | Coaxial |
| Openness: | Closed |
| Installation: | Horizontal |
| Transmission Form: | Worm |
| Samples: |
US$ 325/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do gear drives work in robotic and automated systems?
Gear drives play a crucial role in robotic and automated systems by transmitting motion and power between different components. Here’s a detailed explanation of how gear drives work in these systems:
1. Power Transmission:
– In robotic and automated systems, gear drives are used to transmit power from motors to various mechanical components.
– Electric motors provide rotational motion, which is converted into linear or angular motion by the gear drive.
– The gear drive consists of a set of gears with different sizes and configurations that mesh together to transfer torque and speed.
2. Speed and Torque Conversion:
– Gear drives allow for the conversion of speed and torque between the motor and the driven components.
– By using gears with different sizes (varying number of teeth), the gear drive can change the rotational speed and torque output.
– For example, a gear drive with a larger gear driving a smaller gear will increase the torque while reducing the speed, and vice versa.
3. Motion Control:
– Gear drives enable precise motion control in robotic and automated systems.
– By selecting the appropriate gear ratio, the gear drive can control the speed and position of the driven components.
– Gear drives can be used to achieve smooth and accurate movements, such as in robot arms, conveyor systems, or CNC machines.
4. Reducing Inertia:
– Inertia refers to an object’s resistance to changes in motion.
– Gear drives can help reduce the overall inertia in robotic and automated systems.
– By using smaller gears, the gear drive can reduce the inertia of the driven components, allowing for faster and more responsive movements.
5. Backlash Compensation:
– Backlash refers to the slight play or clearance between gear teeth, which can result in a loss of accuracy and precision.
– Gear drives in robotic and automated systems often incorporate backlash compensation mechanisms to minimize this issue.
– These mechanisms can include preloading the gears or using anti-backlash gears to eliminate or reduce the effects of backlash.
6. Load Distribution:
– In complex robotic systems, multiple gear drives are often used to distribute the load and share the torque among different components.
– This distribution of load helps prevent overloading of individual gear drives and ensures a balanced operation of the system.
7. Redundancy:
– Some robotic and automated systems incorporate redundant gear drives to enhance reliability and fault tolerance.
– Redundant gear drives can provide backup functionality in case of failure or allow for continued operation with reduced performance in the event of a single gear drive failure.
Overall, gear drives are essential components in robotic and automated systems, enabling power transmission, motion control, speed and torque conversion, and load distribution. The specific design and configuration of gear drives in these systems depend on the application requirements, desired performance, and system constraints.

What is the role of gear drives in automotive transmissions?
Gear drives play a crucial role in automotive transmissions. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Speed and Torque Conversion:
– Automotive transmissions use gear drives to convert the engine’s rotational speed and torque into the appropriate output for the wheels.
– By selecting different gear ratios, gear drives enable the transmission to adjust the speed and torque delivered to the wheels based on driving conditions and desired performance.
2. Gear Shifting:
– Gear drives facilitate gear shifting, allowing the driver to select different gear ratios to match the vehicle’s speed and load requirements.
– Depending on the transmission type (manual or automatic), gear drives are responsible for engaging and disengaging the gears during gear shifting operations.
3. Power Transmission:
– Gear drives transmit power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move.
– They transfer torque from the engine’s crankshaft to the transmission output shaft, which is connected to the wheels through the drivetrain.
4. Forward and Reverse Operation:
– Gear drives in automotive transmissions allow the vehicle to move both forward and backward.
– By engaging different gear combinations, the transmission can reverse the direction of power flow, enabling the vehicle to go in reverse.
5. Gear Reduction and Overdrive:
– Gear drives in transmissions provide gear reduction or overdrive capabilities.
– Gear reduction allows the engine to operate at higher RPMs while reducing the output speed, providing more torque for climbing steep inclines or towing heavy loads.
– Overdrive gears, on the other hand, allow the engine to operate at lower RPMs, reducing fuel consumption and engine wear during highway cruising.
6. Synchronizing and Noise Reduction:
– In manual transmissions, gear drives incorporate synchronizer mechanisms to facilitate smooth gear engagements and minimize gear clash.
– These synchronizers match the speeds of the gears before engagement, reducing wear on the gear teeth and enhancing shifting comfort.
– Gear drives can also incorporate noise reduction measures, such as helical or hypoid gears, to minimize gear noise and vibration during operation.
Overall, gear drives in automotive transmissions are essential for speed and torque conversion, gear shifting, power transmission, and enabling the vehicle to move in both forward and reverse directions. They provide the necessary mechanical advantage and flexibility to optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and driving dynamics, making them a fundamental component in the operation of automobiles.
How do you maintain and lubricate gear drives?
Maintaining and lubricating gear drives properly is essential for their smooth operation, longevity, and prevention of premature failure. Here’s a detailed explanation of the maintenance and lubrication practices for gear drives:
1. Inspection and Cleaning:
– Regularly inspect the gear drive for any signs of wear, damage, misalignment, or contamination.
– Clean the gear drive components, including gears, shafts, bearings, and housings, to remove debris, dirt, and old lubricant.
2. Lubrication:
– Select an appropriate lubricant based on the gear drive design, load capacity, operating speed, and ambient conditions.
– Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubricant type, viscosity, and change intervals.
– Apply the lubricant evenly to the gear teeth, shafts, and bearings to ensure proper lubrication and minimize friction.
– Monitor the lubricant level and replenish or change it as needed to maintain optimal lubrication conditions.
3. Temperature Monitoring:
– Monitor the operating temperature of the gear drive using temperature sensors or thermal imaging devices.
– Excessive heat can indicate inadequate lubrication, overloading, misalignment, or other issues that need attention.
– Take corrective measures if the temperature exceeds the recommended range to prevent damage and ensure proper lubrication.
4. Alignment and Adjustment:
– Check and correct gear drive alignment regularly to ensure proper meshing and minimize wear.
– Adjust the gear drive components, such as bearings and shafts, as per the manufacturer’s specifications.
– Misalignment can lead to increased friction, premature wear, and reduced gear drive efficiency.
5. Vibration Analysis:
– Monitor the gear drive for abnormal vibrations using vibration analysis techniques.
– Excessive vibrations can indicate issues like gear tooth damage, bearing failure, or misalignment.
– Address any abnormal vibrations promptly to prevent further damage and maintain smooth operation.
6. Regular Maintenance Schedule:
– Establish a maintenance schedule and adhere to it to ensure consistent and timely gear drive maintenance.
– Include tasks such as lubricant checks and changes, inspections, alignments, and other maintenance activities.
– Keep records of maintenance activities, including lubricant changes, inspections, and repairs, for future reference.
By following these maintenance and lubrication practices, gear drives can operate efficiently, minimize wear and tear, and have a longer service life. It is important to refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and consult with experts when performing maintenance on specific gear drive systems to ensure proper care and optimal performance.


editor by Dream 2024-05-02